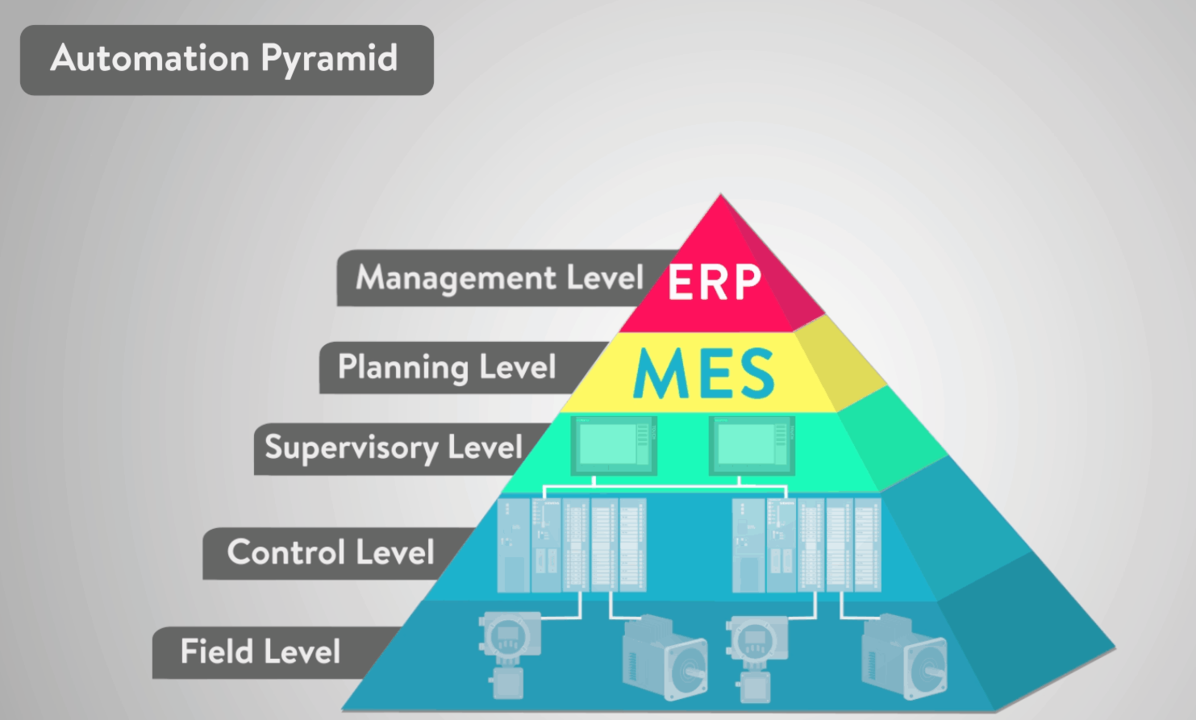
In the vast realm of Industrial Manufacturing, automation plays a pivotal role in streamlining processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring seamless operations. Let’s delve into the world of automation, focusing on key components like PLC, SCADA, DCS, and MES, breaking down these complex terms into simple, easy-to-understand concepts.
“Automation transforms industries, making processes efficient and reliable.”
Understanding Automation
Automation is like having a helping hand in a factory. It involves using machines and technology to do tasks that humans might find repetitive or tricky. In Industrial Manufacturing, this means making things in factories more efficiently and with fewer errors.
PLC: The Brain of Automation
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
Think of a PLC as the brain of the operation. It’s a clever computer that follows instructions to control machines and processes on the factory floor. PLCs are excellent at handling tasks that need to be done over and over again, like assembling parts or checking quality.
SCADA: Keeping an Eye on Things
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)
SCADA is like the eyes and ears of the operation. It helps people see what’s happening in the factory in real-time. It’s a bit like a giant control panel with buttons and screens that let humans monitor and manage the whole production process.
DCS: Coordinating the Orchestra
DCS (Distributed Control System)
DCS is the conductor of the orchestra. It helps all the different parts of the factory work together smoothly. Imagine it as the manager making sure everyone is on the same page, from mixing ingredients to packaging finished products.
MES: Bringing It All Together
MES (Manufacturing Execution System)
MES is like the coordinator at a big event. It helps plan, track, and make sure everything is happening as it should. MES connects with PLC, SCADA, and DCS to ensure all tasks are carried out efficiently and on time.
How Automation Works Together
In an automated factory, PLC, SCADA, DCS, and MES work as a team. PLC controls the machines, SCADA keeps an eye on them, DCS ensures everything runs smoothly, and MES manages the entire production process.
Benefits of Automation
- Increased Efficiency: Automation helps factories produce more goods in less time, reducing costs and wastage.
- Improved Quality: With precise control from PLCs, the chances of errors are minimized, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Enhanced Safety: Automation takes care of dangerous tasks, keeping workers safe from harm.
- Real-time Monitoring: SCADA allows instant oversight, helping identify and address issues promptly.
- Better Collaboration: DCS ensures seamless communication between different parts of the manufacturing process.
- Effective Planning: MES helps in planning and optimizing production schedules, ensuring smooth operations.
Challenges and Solutions
- Initial Costs: Implementing automation can be expensive, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the upfront investment.
- Employee Training: Workers may need to learn new skills, but proper training programs can address this challenge.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular maintenance is essential, but it ensures the longevity and reliability of automated systems.
The Future of Automation in Manufacturing
As technology advances, automation in Industrial Manufacturing is expected to become even more sophisticated. Integration of artificial intelligence, data analytics, and robotics will further revolutionize how factories operate, making processes more efficient and responsive.
Practical Application
Let’s imagine a biscuit factory using automation. PLC guides the machines to mix ingredients precisely, SCADA monitors the temperature and quality in real-time, DCS ensures the ovens and packaging work together flawlessly, and MES plans the production schedule. This results in tasty biscuits made efficiently with consistent quality.
Real-world Impact
In a real-world scenario, a car manufacturing plant employs automation. PLC controls robotic arms assembling parts, SCADA keeps an eye on the production line, DCS ensures synchronized operations, and MES manages the entire process. The impact is significant—cars are produced faster, with fewer errors, ensuring a smoother manufacturing process.
“In the age of technology, PLC, SCADA, DCS, and MES redefine the future of manufacturing.”
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Manufacturing
In the dynamic landscape of Industrial Manufacturing, embracing automation is not just a choice but a necessity for staying competitive. PLC, SCADA, DCS, and MES, though sounding complex, are the backbone of this transformation, ensuring a smoother, more efficient, and error-free production journey. As we move towards a future where technology continues to evolve, the role of automation in shaping the manufacturing industry remains indispensable.

Siemens PLC Systems

Siemens SIMATIC HMI
Automation























