In the dynamic world of industrial manufacturing, the concept of control systems plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency, precision, and optimal performance. Let’s delve into the basics of control system from an industrial manufacturing perspective, demystifying the technical jargon for a clearer understanding.
“Control systems are the unsung heroes of manufacturing, ensuring precision and efficiency in every operation.”
Understanding Control Systems
Control systems are the invisible maestros behind the scenes, orchestrating the functions of machines and processes in industrial settings. At its core, a control system manages and regulates the behavior of other systems to achieve desired outcomes. In the context of industrial manufacturing, these systems govern machinery, ensuring they operate in a synchronized and controlled manner.
Types of Control Systems
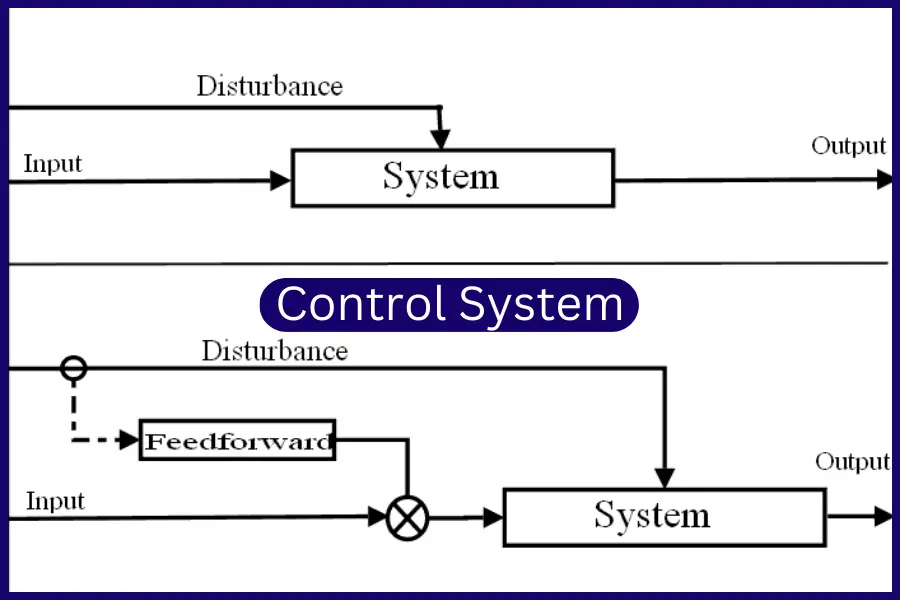
Open-Loop Control System
Imagine a one-way street with no traffic lights – that’s the essence of open-loop control. In industrial manufacturing, this system operates without feedback, meaning it executes commands without actively monitoring the output. While simple, it lacks the adaptability needed for complex processes.
Closed-Loop Control System
Closed-loop control, on the other hand, introduces a feedback mechanism. It constantly assesses the output and adjusts the input accordingly, creating a dynamic and responsive system. This type of control is like having traffic lights on that one-way street – adapting to changes in real-time for a smoother flow.
Components of a Control System
Sensors
Sensors act as the eyes and ears of a control system, collecting data from the environment or the machinery itself. In an industrial manufacturing setup, sensors detect variables such as temperature, pressure, or speed, providing crucial input for decision-making.
Actuators
Actuators are the muscles of the control system. They receive signals from the controller and execute the necessary actions. In manufacturing, actuators could be motors adjusting the speed of a conveyor belt or valves regulating the flow of liquids.
Control System in Action: A Practical Example
To illustrate the importance of control system in industrial manufacturing, let’s consider a conveyor belt transporting goods along an assembly line.
Setpoint
The control system begins by defining a setpoint – the desired speed at which the conveyor should operate. This is the target that the system aims to achieve.
Controller
The controller is the brain of the operation. It receives input from sensors monitoring the conveyor’s speed and compares it to the setpoint. If a variance is detected, the controller sends signals to the actuators.
Actuators in Action
In response to the controller’s signals, the actuators adjust the speed of the conveyor. If it’s lagging, they increase the speed; if it’s exceeding the setpoint, they slow it down. This continuous feedback loop ensures the conveyor operates at the desired speed.
Importance of Control System in Industrial Manufacturing
Precision and Consistency
Control system eliminate the guesswork, providing a level of precision that human intervention alone cannot achieve. This is crucial in manufacturing, where consistency is key to product quality.
Increased Efficiency
By automating processes and minimizing deviations, control system enhance overall efficiency. They optimize resource utilization and reduce the likelihood of errors, leading to cost-effective production.
Fault Detection and Correction
Control systems are equipped with mechanisms to detect anomalies. If a deviation occurs, the system can trigger alarms or take corrective actions, preventing potential damage and downtime.
Challenges in Control Systems
Sensitivity to External Factors
Control systems can be sensitive to external disturbances, such as fluctuations in power supply or environmental conditions. Engineers must account for these variables to maintain system stability.
Complexity and Maintenance
As control systems become more sophisticated, their complexity increases. Regular maintenance and updates are crucial to ensure optimal performance and adaptability to evolving manufacturing processes.
Future Trends in Control Systems
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The future of control systems in industrial manufacturing is closely tied to AI. Smart systems capable of learning and adapting in real-time will revolutionize how factories operate, further enhancing efficiency and responsiveness.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of IoT technologies allows for seamless communication between various components of a control systems. This interconnectedness enhances data exchange and enables more informed decision-making.
Practical Application
Let’s imagine a bakery as our practical example. The control systems here is like the skilled baker overseeing the oven temperature. If the temperature goes below the setpoint, the controller (our baker) instructs the oven to heat up. If it surpasses the setpoint, the baker takes action to cool it down. This ensures every batch of delicious cookies comes out perfectly baked, just like control systems ensure machinery operates at the right speed in manufacturing.
Real-world Impact
In a car assembly line, think of the control systems as the traffic controller at a busy intersection. It monitors the flow of cars (products), adjusting signals to avoid jams or collisions. The impact? Smooth traffic, efficient production, and happy customers receiving their cars on time.
“In the industrial orchestra, control systems play the conductor, harmonizing machinery for optimal performance.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, the basics of control system in industrial manufacturing are the backbone of efficient and precise production processes. From open-loop to closed-loop control, sensors to actuators, these systems ensure the seamless operation of machinery. Simply put, when engineers and manufacturers grasp the importance of control system and keep up with the latest trends, they can use these systems to drive the industry forward. It’s like having a key to unlock a future where things work even better and new, exciting ideas can flourish.
Automation























